Humans are making things as per their requirements. Primitive humans made weapons with wood and stone, made wheels after that they gradually made things with metals. Making things has been an essential activity of human civilizations since before recorded history.
Today, the term manufacturing is used for this activity. For technological and economic reasons, manufacturing is important to the welfare of all of us.
What is Manufacturing Process?
Making things has been an essential activity of human civilizations since before recorded history. Today, the term manufacturing is used for this activity. The word manufacture is derived from two Latin words, manus (hand) and factus (make); the combination means made by hand. In the modern context, it involves making products from raw material by using various processes, by making use of hand tools, machinery, or even computers.
Technologically, manufacturing Processes are the application of physical and chemical processes to alter the geometry, properties, and/or appearance of a given starting material to make parts or products; manufacturing Processes also include assembly of multiple parts to make products. The Manufacturing processes involve a combination of machinery, tools, power, and labor. Manufacturing Processes are almost always carried out as a sequence of operations. Each operation brings the material closer to the desired final state.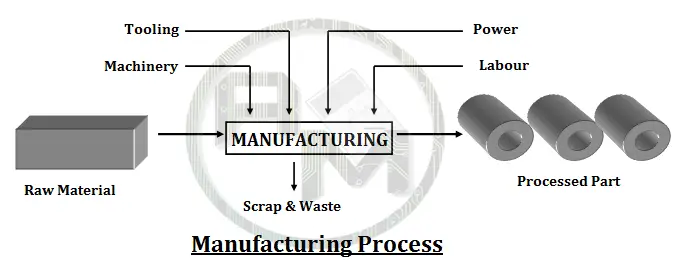
Economically, the Manufacturing Process is the transformation of materials into items of greater value by means of one or more processing and/or assembly operations. Manufacturing Processes adds value to the material by changing its properties and shape, or by combining it with other materials that have been similarly altered. The material has been made more valuable through the manufacturing operations performed on it. When plastic is molded into the complex geometry of a table, it is made even more valuable.
Manufacturing examples
Cell Phone/ Mobile, Digital Camera, Cars, Motor Bikes, Automotive spare parts, Ball Pen, High Definition Television, Home security system, Inkjet color printer, Industrial Robot, MRI Machines, Medicines, Beverages, Supersonic aircraft, PVC film, hardware, and many more.
History of Manufacturing
Today, Manufacturing is a very complex and intricate process that requires various processes necessary for the production of a product and its components. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, manufacturing simply meant creating products or goods by hand. Some of the processes—casting, hammering (forging), and grinding—date back 6000 years or more. The ancient Indians & Romans had what might be called factories to produce weapons, scrolls, pottery and glassware, sculptures, and other products of the time, but the procedures were largely based on handicrafts. An Indian sculpture of Dancing shiva was found in the 5th century. Well, we leave the old historical things and move on to the History of modern manufacturing Processes.
Here are some historical events and discoveries that have a major impact on the development of modern manufacturing systems.
The Principle of Division of Work –
dividing the total work into tasks and assigning each worker to become a specialist at performing only one task.
The Industrial Revolution (1760–1830)-
had a major impact on production in several ways. It marked the change from an economy based on agriculture and handicraft to one based on industry and manufacturing. The change began in England, where a series of machines were invented and steam power replaced water, wind, and animal power. These advances gave the British industry significant advantages over other nations, and England attempted to restrict the export of the new technologies. However, the revolution eventually spread to other European countries and the United States.
James Watt’s steam engine-
Power-generating technology for the industries and was one of the driving forces of the industrial revolution.
Machine Tools-
John Wilkinson first used a boring machine in 1775. Later on a lot of machine tools later like lathe machine, Milling, Drilling, Pressing Machines, etc were introduced.
The spinning jenny-
invented in 1964 & one of the key development in the textile industry for increment in production and quality. This was a huge change in the textile industry and changed the way of production. Before then the production of clothes was a very time-consuming process.
The Factory System-
a new way of organizing large numbers of production machinery & workers and based on the division of labour.
Second Industrial Revolution-
In this era, most of the scientific management systems introduced like Motion Study, Time Study, Piece rate system, Incentive system, Use of data collection, Recordkeeping, etc.
The Assembly line-
Henry Ford (1863–1947) introduced the assembly line in 1913. The assembly line made possible the mass production of complex consumer products. In an assembly line, parts are moving from one work-station to the next work-station. At a specific work-station, each worker assigned to do a specific task to add more parts to make a complete final assembled product.
Basic Classification of Manufacturing Technologies
Manufacturing technologies have always been improving over time. There has been a big difference in the way of making things fast, durable, and cost-efficient. According to the latest manufacturing environment, these technologies may be divided into three fundamental categories as following
Subtractive manufacturing technology
In Subtractive manufacturing technology, the desired geometry is obtained by the defined removal of material. These are the most convenient method of manufacturing. Material removal is done by machining tools such as Lathe-machine, CNC turning, Milling Machine, Honing machine, etc. for example, all the machining processes such as by turning, milling, stamping, etc.
Formative manufacturing technology
Formative manufacturing means to alter the geometry in a defined way by applying external forces or heat, for example, by injection molding, forging, or casting.
Additive manufacturing technology
Additive manufacturing creates 3-dimensional objects by depositional materials such as proper polymers, ceramics, or metals in multiple layers of equal thickness. These objects are built layer by layer which is in contrast to traditional manufacturing that often requires machining or other techniques to remove surplus material. Therefore it is also called layer technology and this process called the 3D printing process.
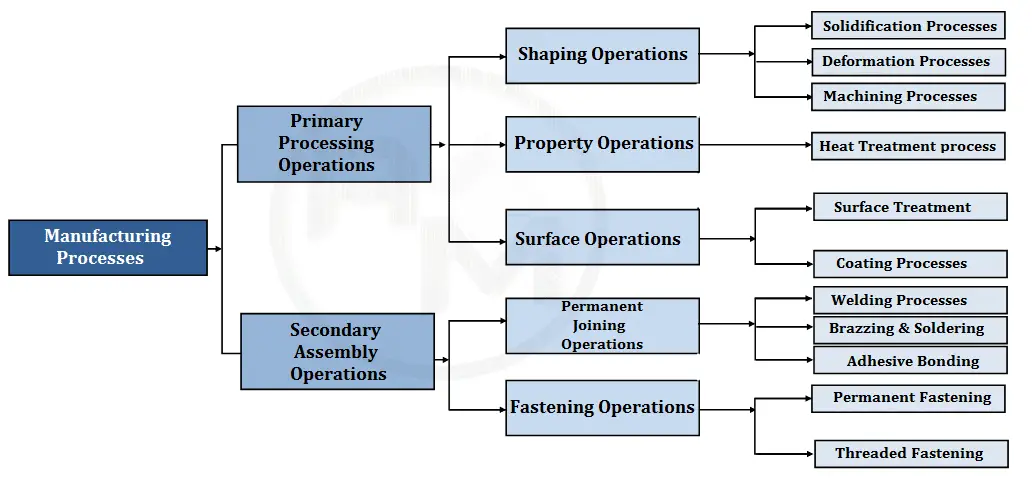
Broad classification of Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing Processes may be classified into two following categories:
Primary Processing Operations
A processing operation uses energy to Obtain the desired shape. The forms of energy include mechanical, chemical, electrical, and other energy. The energy is applied in a controlled way by means of machinery, tooling & Humans. Human energy may also be required, but the workers generally control the machines, take care of the operations, and load and unload parts before and after every cycle of operation.
Three categories of processing operations are distinguished:
- Shaping Operations
- Property Operations
- Surface Operations
 Shaping operations:
Shaping operations:
Shaping Operations change the geometry or shape of the starting work material by various procedures. Common shaping processes are Casting, Forging, Machining, Stamping. Most shape processing operations required heat, mechanical force, or a combination of these to effect a change in the shape of the material. There are various ways to classify the shaping processes as follows.
- Solidification Processes
- Deformation Processes
- Machining Processes
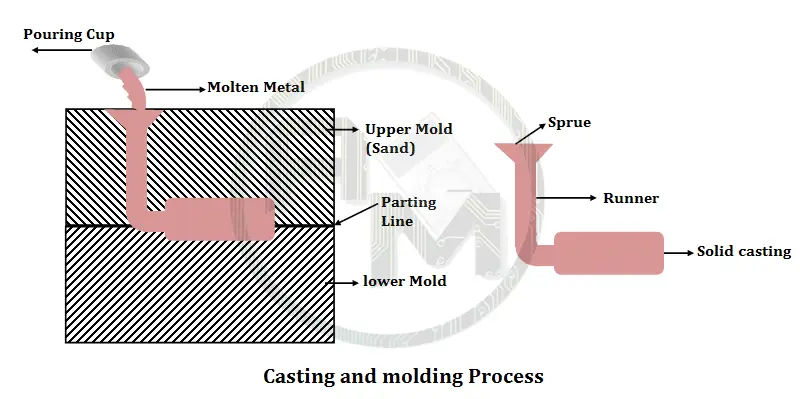
Solidification Processes:
In these processes, the Material is heated to liquidity or highly plastic (semifluid) state. Materials in a liquid or semifluid form, they can be poured or otherwise forced to flow into a mold cavity. As temperature decreased, metal taking a complex solid shape the same as the cavity, most processes are called casting or molding. Casting is used for metals, and molding for plastics.
Deformation Processes:
In deformation processes, the shape of the metal is altered by the application of forces that exceed the material’s yield strength. Deformation processes include Stamping, Rolling, Extrusion, and Forging operation to alter the shape of the material. During deformation, Materials must be sufficiently ductile to avoid fracture. Material is often heated to increase ductility before deforming.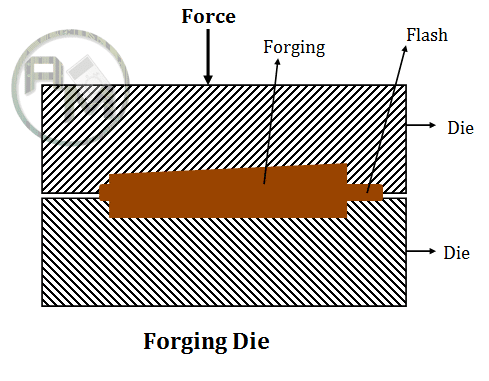
Note: The powder metallurgy process is somewhere between the Solidification process and the deformation process.
Machining Processes:
A large number of components require further processing after the solidification and deformation processes. These components are subjected to one or more number of machining operations to obtain the desired shape and dimensional accuracy on flat and cylindrical jobs. Thus, the jobs undergoing these operations are the roughly finished products received through previous processes. This can be done by a manual process or by using a machine called machine tool like lathe, milling machine, drilling, shaper, planner, slotter machine. A lot of material waste as scrap in the machining process.
Some of the common secondary or machining processes are—
(1) Turning (2) Milling (3) Threading (4) Drilling (5) Boring (6) Shaping (7) Slotting (8) Hobbing (9) Grinding (10) Gear cutting (11) Unconventional machining processes namely machining with Numerical Control (NC), (12) machines tools or Computer Numerical Control (CNC) (13) machines tools using Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) (14) Electrochemical Machining Process (ECM) (15) Thermal Material Removal Processes (EDM, EBM, LBM), etc.
Property- operations:
The second major type of processing operation is Property operations. Property operations improve the mechanical or physical properties of the work material without altering the shape of the part. Heat Treatment is the most important property enhancing operation.
Heat treatment is a heating and cooling process of a metal or an alloy in the solid-state with the purpose of changing their properties like softness, hardness, tensile strength, toughness, etc. The following are common processes: Annealing, Normalising, Hardening, Case hardening, Flame hardening, Tempering, Shot peeing, Grain refining Vaccum Hardening, and Age hardening.
Surface Operations:
The processes to remove dirt, oil, and other contaminants from the surface. Surface treatments include mechanical working such as shot peening and sandblasting, and physical processes such as diffusion and ion implantation. Coating and thin film deposition processes apply a coating of material to the exterior surface of the work part. Surface processing operations may be classified into the following categories:
- Cleaning & Other Surface Treatments
- Coating
Some of the commonly used surface finishing processes are:
Honing, Lapping, Belt Grinding, Polishing, Sanding, deburring, Electroplating, Buffing, Metal spraying, Painting, Coating, Anodizing, Galvanizing, Plastic coating, Sandblasting, etc.
Secondary Assembly Operations:
An assembly operation joins two or more separate components to create a new entity. Components of the new entity are connected either permanently or semi-permanently.
Permanent joining processes include welding, brazing, soldering, and adhesive bonding. They form a joint between components that cannot be easily disconnected.
Some assembly components/ Products are fastened together in a joint that can be conveniently disassembled. Screws, bolts, and other threaded fasteners are important traditional methods in this Semi-permanent assembly category.
What is the Manufacturing Support Systems?
The basic required functions for manufacturing processes facilities are the following:
- Design the Product & Process, Set-up Equipment & Quality standards: R&D
- Production Planning and Control: PRODUCTION
- Maintain product quality standards: QA & QC
These functions are accomplished by procedures and peoples who manage the production operations.
Research and development (R&D) Department
R&D is responsible for the activities companies undertake to innovate and introduce new products, planning the manufacturing processes—deciding what processes should be used to make the parts and assemble the products, Stay ahead of manufacturing trends. R&D is also involved in Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) and Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). It is often the first stage in the development process and plays an integral role in the life cycle of a product.
Production Department
A production department is a group of following functions within a manufacturing facility.
Production planning and Control: Schedule the production plan for each product, Manage inventory & take corrective measures if necessary.
Production execution: Execute the production plan, Inventory Management, Management of equipment, machinery, and manpower as per the situation.
Maintenance: Takes corrective measures if the machine breaks down. Preventive & Predictive maintenance to reduce the breakdown of machinery and equipment. Manage all necessary spares parts of machinery.
Purchase & Store: Purchase & Store department is responsible for procuring all necessary materials needed for production or daily operations.
Logistics & dispatch: The primary duty of the logistics department is to ensure geographical repositioning of finished products, raw materials, equipment & machinery, or scrap.
Quality Assurance / Quality Control
Every industry must pay sufficient attention to maintaining quality because it is another important requirement or function of a Manufacturing unit. The key responsibility of QA/QC is to ensure the quality of products manufactured by their company.
- Perform and coordinate inspections and determine quality assurance testing models of raw materials and finished products.
- Prepare, document, and execute detailed test plans, test cases, and defect reports as per ISO standards.
- Review and approve quality requirements for manufacturing planning, supplier purchase orders, and engineering specifications.
- To perform training to workers for producing good quality products.

