Production planning and scheduling are two important subset processes of operations management to increase efficiency in manufacturing and improve effectiveness in customer service. Production planning determines what, when, and how much to produce to meet the customer’s needs, without excessive inventory or backorder costs.
Scheduling determines how to achieve the goals set in production planning when the resources are limited; and, if the goals cannot be realized, how best to set new goals that are optimum and practical with the available resources.
What is Production Planning Process?
As per Wikipedia“Production planning is the planning of production and manufacturing modules in a company or industry. It utilizes the resource allocation of activities of employees, materials, and production capacity, in order to serve different customers.“
In detail,
The production planning process is the planning of the various production modules in the manufacturing industry to utilize all resources like manpower, materials, and machines in order to serve different customers. Production Planning includes forecasting of customer orders, determination of plant capacity, long-range and short-range planning, involving topics such as production planning, inventory control, and scheduling.
Production planning includes decisions generally consists of the planning of the following :
- Routing,
- Scheduling,
- Dispatching,
- Inspection,
- Coordination and control of materials,
- Methods,
- Machines & tools,
- Operating times.
The ultimate objective is to define the organization of the supply and movement of materials, labour, machine utilization, and other related activities in order to bring about the desired manufacturing results in terms of quality and quantity in expected time and place.
Production planning starts with market demand estimation. Market demand depends on various factors such as changing consumer taste, economy, and different seasons in a year. The demand prediction is called the Forecasting. There are different forecasting techniques that can be used to make good demand predictions to match production with respect to the demand at that time.
Production planning is usually done at an aggregate level, for both products and resources. Products to be manufactured are combined into aggregate product families that can be planned together so as to reduce planning complexity. Similarly, production resources, such as machines or man-hours, are aggregated. While performing this aggregation, specific attention is required to assure that the resulting aggregate plan can be reasonably disaggregated into feasible production schedules.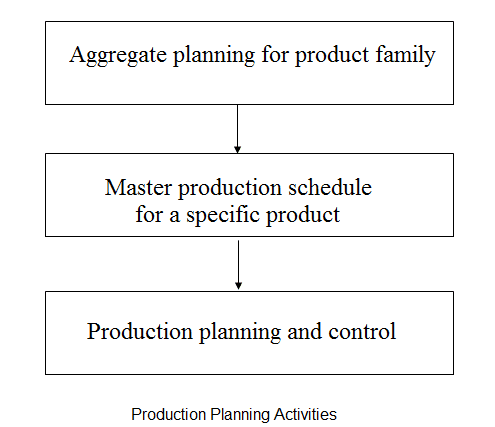 Production planning is considered differently in various levels of the organizations. At the operational level production scheduling takes place. In order to do so, there is a “need to know” capacity and available resources as well as master production plans indicating the overall production amount for a certain planning period. The master plan should be generated from aggregate planning which will, in turn, be based on demand forecasts for a particular set of products.
Production planning is considered differently in various levels of the organizations. At the operational level production scheduling takes place. In order to do so, there is a “need to know” capacity and available resources as well as master production plans indicating the overall production amount for a certain planning period. The master plan should be generated from aggregate planning which will, in turn, be based on demand forecasts for a particular set of products.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is transforming the inputs into respective products through several processes as designed in accordance with the manufacturing processes and production plans.
Quality management
Quality Management is a systematic process that translates quality policy into measurable objectives and requirements and identifies the sequence of steps for realizing them within a specified time period. It includes creating and managing methods, criteria, and techniques that ensure an output fits the intended purpose, and meets a stated expectation, and is accepted by the program.
It assures that the products produced are within the tolerance limits and shifted to the customer as error-free. It also includes making plans and corrections on the process in such a way that faulty products are not produced at all. Quality management mainly includes tree basic set of activities including:
- Quality planning
- Quality assurance
- Quality control.
Each of these sets of activities intends to sustain the overall quality of the manufacturing processes as well as products produced by those processes.
Storing and shipment
Storing and shipment operations are to keeping products and raw material in stock or transferring them to the customers. These operations management includes material handling planning, Inventory management, dispatch, and transportation planning.
What is the Master Production Schedule (MPS)?
With expected demand as an input to production and aggregate planning, all resources necessary to meet the demands and plans for the future are evaluated. These might include capital investment, labor force, full-time and/or parttime workers, overtime, and subcontracting. The outcome of aggregate planning is a master production schedule (MPS).
Every production planning and control system begins with the marketplace. Marketplace demand is an independent demand that relies heavily on factors such as changing consumer taste, different seasons in a year, the ups and downs of the national economy, and even political winds. With varying demand, it is important to match production with respect to the demand at that time.
Different forecasting techniques can be used to make good demand predictions. With expected demand as an input to production and aggregate planning, all resources necessary to meet the demands and plans for the future are evaluated. These might include capital investment, labor force, full-time and/or parttime workers, overtime, and subcontracting. The outcome of aggregate planning is a master production schedule (MPS).
The scope of the Production planning process
The scope of the Production planning process includes many activities and responsibilities that depend on the type of production operations accomplished by the organization. The usual activities include the following:
Design for manufacturability
The objective is to develop product designs that not only meet functional and performance requirements, but that also can be produced at a reasonable cost with minimum technical problems at the highest possible quality in the shortest possible time.
Process planning
Process planning is the principal activity of manufacturing. Process planning involves determining the most appropriate manufacturing processes and the order in which they should be performed to produce a given part or product specified by design engineering.
Process planning includes the following processes :- Deciding what processes and methods should be used and in what sequence
- Determining tooling requirements
- Selecting production equipment and systems, and
- Estimating costs of production for the selected processes, tooling, and equipment.
The process plan must be developed within the limitations imposed by available processing equipment and the productive capacity of the factory.
Problem-solving and continuous improvement
These process includes solving technical production problems. It should also be engaged in continuous efforts to reduce production costs, increase productivity, and improve product quality. Problem-solving and continuous improvement processes are the responsibility of the Quality department and the maintenance department.
Generally, the Problem-solving & Improvement process has five various stages as following:- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control

