“Industrial maintenance is the process of keeping machines, equipment, and assets used in manufacturing or other industrial processes in good working condition through routine inspections, cleaning, lubrication, repair, and replacement of parts to ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency of industrial processes while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.”
We often heard about Maintenance in our daily life, it is an important process to keep something functional. It can be in the industry or in household appliances. No machine can work for a long time without proper maintenance.
In this article, we are going to discuss various methods used for maintaining machines in working conditions in industry, i.e industrial maintenance.

What is Industrial Maintenance
The technical meaning of Industrial Maintenance is ” the practice of keeping the equipment and machines in proper functioning condition to produce quality products”. The Objectives of industrial maintenance is to increase plant equipment’s life & keeping all the plant’s assets in good condition at the lowest possible cost. Industrial Maintenance is also called “Plant Maintenance“.
Industrial Maintenance includes two following actions:
- Control or prevent the deterioration process leading to failure of a machine or equipment.
- Restore the object to its operational state through corrective actions after a breakdown or failure.
Industrial Maintenance involves regular & routine Cleaning, checking, servicing, repairing, or replacing the parts in order to prevent the breakdown of a machine Or machine tool. It is also very important to keep all the records of Spare parts, Due & Last service & repair of machines, Equipment history, Equipment’s Manuals, etc.
The need for Industrial Maintenance
In manufacturing, equipment and machines are very important resources that are constantly used for producing products. So, these must be kept in the best operating condition. Otherwise, Poor working of machines & equipment will lead to quality-related problems or there will be excessive downtime and also interruption of production if it is used in a mass production line. Hence, Industrial maintenance is necessary to maintain the equipment in good operating conditions.
In certain cases, the equipment will be obsolete over a period of time. If a company wants to be in the same business competitively, it has to take a decision on whether to replace the equipment or to retain the old equipment by taking the cost of maintenance and operation.
5 Stages of Breakdown of machines
Why does the machine stop working? The simplest and direct answer is “deterioration”. From the day a machine is installed, its condition gradually deteriorates over the years of use, and sooner or later the single or combination of deteriorated/worn out parts will cause the machine to break down.
Almost every machine has symptoms of ill health before it breaks down. There are 5 stages of a machine on the path of Break down are following. The industrial maintenance team must recognize where each machine is on that path.
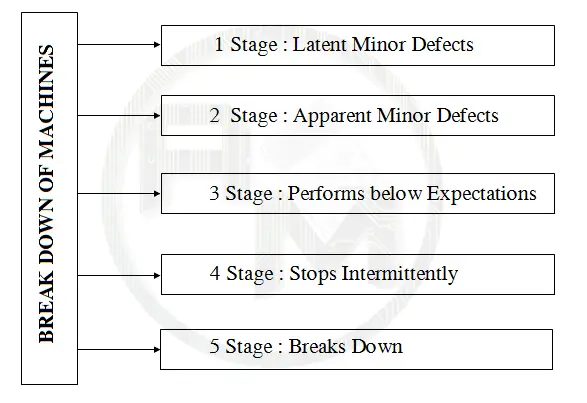
Latent Minor Defects: At this very first stage where it’s very hard to recognize the defect by ear or eye of the industrial maintenance team. But the machine’s rotating parts are operating under increasing friction and its fastened parts are getting a little looser. Only experienced industrial maintenance peoples detect those faults at the first stage.
Apparent Minor Defects: Now those defects at the first stage become somewhat noticeable by the ear or eye of the industrial maintenance team. In addition, the machine may be vibrating more, making more noise, and leaking small amounts of oil, water, or air. But none of these defects are major enough to impair the machine’s functioning.
Performs below Expectations: Now Machine performs with the less desired precision. It’s hard to maintain dimensional tolerances at this stage. The machine is turning out products with widely varying quality and suddenly it needs more adjusting than it used to require. It can no longer keep up with quality standards. The industrial maintenance team must take appropriate action at this stage to counter the breakdown of the machine.
Stops Intermittently: At this stage, the Machine usually demands frequent shutoffs to make adjustments and repairs. but can be started up again after making simple adjustments or repairs. It is not good for manufacturing operations as the Rate of production is much affected and breakdown time increases.

Breaks Down: At this final stage, the machine functions so poorly that it stops itself, which is to say it breaks down. Generally in the Breakdown stage machines required to replace their spare parts.
Types of industrial Maintenance
The life of most machines & equipment requires regular maintenance like appropriate lubrication on rotating components, Belts adjustment, alignment, components replacement, servicing of engine, etc. These activities provide the maximum life of a machine or equipment and prevent them from breakdown as machine breakdowns are the inevitable facts of Manufacturing.
When we let factory equipment deteriorate, sooner or later it will break down. In view of this, how can we achieve zero breakdowns? We must take measures to halt or slow equipment deterioration before it reaches the breakdown stage. So there are three industrial maintenance activity approaches as follows:
- Break Down Maintenance or Reactive/ Real-time Maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance
What is Breakdown Maintenance Or Reactive / Real-time Maintenance
“Breakdown maintenance comprises the maintenance procedures taken in response to a breakdown.” Replacement of worn-out Punches in stamping tools, Electric motor failures, Misalignment of components are examples of common real-time breakdowns and required real-time/breakdown/corrective maintenance.
This type of maintenance activity generally corrects problems for a long time ( Replacement of worn-out spares part), thus also called Corrective Maintenance.
Note: When machines do their job, they are bound to deteriorate, however, they could have been saved from breakdowns through preventive and predictive maintenance but Preventive and predictive maintenance cannot be 100% breakdown-proof for machines.
What is Preventive Maintenance
“Actions performed on a time or machine-run-based schedule that detect, preclude, or mitigate degradation of a component or system with the aim of sustaining or extending its useful life through controlling degradation to an acceptable level.” Called the Preventive Maintenance.
Once a breakdown occurs, we must find the cause and make an improvement that will prevent the same kind of breakdown from occurring again. To do this, the people who are dealing with the breakdown must see it first hand, and then make a decision about how to respond effectively to the problem.
What is Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance can be defined as “Measurements that detect the onset of a degradation mechanism, thereby allowing causal stressors to be eliminated or controlled prior to any significant deterioration in the component physical state. Results indicate current and future functional capability”.
Difference Between Predictive and Preventive Maintenance
Basically, predictive maintenance differs from preventive maintenance by basing maintenance need on the actual condition of the machine rather than on some preset schedule. Preventive maintenance is time-based.
Activities such as changing lubricants are based on time, like calendar time or equipment run time. For example, most people change the oil in their vehicles every 3,000 to 5,000 km traveled. This is effectively basing the oil change needs on equipment run time.
No concern is given to the actual condition and performance capability of the oil. It is changed because it is time. This methodology would be analogous to a preventive maintenance task. If, on the other hand, the operator of the car discounted the vehicle run time and had the oil analyzed at some periodicity to determine its actual condition and lubrication properties, he may be able to extend the oil change until the vehicle had traveled 10,000 km. This is the fundamental difference between predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance.
Industrial Maintenance Costs
Generally, the cost of Corrective maintenance is 5 to 20 times greater than the cost of the effort that would have prevented the failure or breakdown (Preventive & Predictive Maintenance). The loose screws, worn-out v-belts, springs, or other parts replaced and greasing of moving parts of the machine are also done in Preventive Maintenance and predictive maintenance. Preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance prevent the deteriorating of the complex and expensive parts of the machine and increase the life of them. In this way, the cost of industrial maintenance can be reduced.
When the cost of the loss of product, business opportunity, loss of clients, and similar indirect costs are added to the cost of the repair we can begin to see how the true cost of reactive maintenance practices can quickly add up. Hence, the costs of industrial maintenance may be divided into two major categories:
Direct costs:
These Industrial maintenance costs are incurred due to maintenance and repair actions, broadly represented by the cost of labor, the cost of material and spare parts, the cost of contractors, and the costs of infrastructures used and related tax (service tax, etc.). Often, these are the costs that may be tracked down easily into account books.
Indirect costs:
These industrial maintenances are costs resulting from the consequences associated with failure or unplanned maintenance actions and include loss of revenue due to the production stops owing to maintenance and repair actions, cost of accidents, demurrages, insurance policies, and so on.
Objectionable conditions in manufacturing floor
Whether the factory uses small machines or large ones, there is no excuse for breakdowns. It is not hard to come up with this list of 16 objectionable conditions to avoid a possible break down and saves the precious time & efforts of the industrial maintenance team.
- Metal shaving scattered all over the machine and floor.
- Machines so dirty that peoples avoid touching them.
- Level gauges are hard to read because of dust and oil.
- Leaks in hydraulic and pneumatic equipment.
- Loose fasteners ( Nut, bolt, screws).
- Strange noises coming from the machine.
- Muddy oil in oil tanks.
- Machine vibrating abnormally.
- Abnormally hot motor.
- Sparking in wires.
- Loose V belt.
- Floors dirtied by puddles of oil leaked from machines.
- Clogged air ducts that emit dust into the room.
- Broken gauges and measuring instruments still being used.
- Cracks filled with temporary repairs like cardboard.
- Use of damaged spare parts.
3 key points in Industrial Maintenance
Since industrial maintenance is a very broad and complex process that includes servicing, repairing, Prediction & Planning of maintenance, tracking, and maintain the consumable spare parts and tools ( cutting wheels, screws, nuts, springs, v-belts, grease, etc). So industrial maintenance may be a very hard and difficult task in many circumstances. when a machine got a breakdown, it affects the whole manufacturing operations including timely dispatch or less-quality products. The Industrial maintenance team must remember the following three key points to avoid the hassle.
Cleanliness:
Machine operators and industrial maintenance technicians need to fully recognize the importance of maintaining cleanliness and make it just as much a part of their daily routine. Maintaining cleanliness is not something to be done at the odd moment between one production operation and the next. Instead, we should view it as an essential part of pre-production activities.
Benefits of cleanliness:
- The neat and clean machine will have a higher production rate.
- A neat and clean machine will turn out fewer defective products by bringing better quality products.
- A neat and clean machine will cause fewer injuries as dusty and oily surfaces to cause injuries on the shop floor.
- A neat and clean machine will bring better maintenance options as it is quite easy to understand that a dirty oil tank leakage or air leakage will harder to find out for the Industrial maintenance team.
Checking:
Industrial Maintenance should be understood as an activity designed to prevent equipment or machine from breaking down. The purpose of checking is to determine whether the equipment is about to break down. Since the operator is the one who knows best how well or poorly the machine is operating, the operator has the kind of concrete problem-consciousness needed for effective daily checking and, when necessary, inform the industrial maintenance team.
Oiling:
The industrial maintenance technician or machine operators need to give each machine just the kind of oil it needs, just when it is needed, and in just the amount needed. Oiling and greasing of machines is a primary maintenance activity. It is so important for the industrial maintenance team that only oiling and greasing can decreased breakdowns by 25%. Oiling and greasing of rotating or moving components reduce the friction and noises. Also, reduce Wear & tear which is good for manufacturing processes.


One Comment