Ever seen small bulbs probably in size of a millimeter that we mostly use in decorating our house, shop, etc in Christmas, New Year, Diwali, or any other occasion? They are LED Bulbs.
Though very tiny but they glow brightly in the dark. Some of them just glow constantly, and some of them switch their state On/Off and vice-versa. I hope you have got an idea of what we are going to discuss in this article. If not, see the image below for better understanding. Yes, we are going to learn about Light Emitting diodes and LED lights their working, and how they are constructed. But first, let’s learn about its definition.

What is Light Emitting Diode- LED Definition:
A light emitting diode is a semiconductor device. It is a PN junction that emits or produces light when an electric current passes through it. The LED lighting can be more versatile, efficient and long-lasting as compared to compact fluorescent lighting. This type of diode emits narrow bandwidth of visible light or invisible light at different color wavelengths for remote control. It is preferable because it is small in area and to shape its radiation pattern many optical components may be used.
Led Diagram and Construction
Now that you know what is a Light-emitting diode, it is time to understand its basic construction. We have included a simple diagram to make you understand it easily.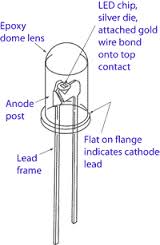 The construction of LED differs from the normal standard diode in many aspects. As shown in the figure on the right side, the p-n junction of the LED bulb is enclosed by a transparent, hard plastic epoxy resin hemispherical-shaped shell or body which protects the Led from shock and vibration. LEDs have two terminals; a cathode and an anode. The cathode terminal is identified by either a flat spot on the body or notch or by one of the leads shorter than the other. The domed top of the LED is just like a lens concentrating the amount of light. Identifying Cathode and Anode: A Cathode lead of LED Bulb is always shorter than the Anode. If you can not identify like this, use a digital multimeter for ease. Read our article on using a multimeter.
The epoxy resin shell is constructed in such a way that the photons of light emitted by the junction are reflected away from the substrate base to which the diode is attached because Led junction does not emit that much light. Due to this, the brightest light will be emitted at the top of the Led. [Image source]
The construction of LED differs from the normal standard diode in many aspects. As shown in the figure on the right side, the p-n junction of the LED bulb is enclosed by a transparent, hard plastic epoxy resin hemispherical-shaped shell or body which protects the Led from shock and vibration. LEDs have two terminals; a cathode and an anode. The cathode terminal is identified by either a flat spot on the body or notch or by one of the leads shorter than the other. The domed top of the LED is just like a lens concentrating the amount of light. Identifying Cathode and Anode: A Cathode lead of LED Bulb is always shorter than the Anode. If you can not identify like this, use a digital multimeter for ease. Read our article on using a multimeter.
The epoxy resin shell is constructed in such a way that the photons of light emitted by the junction are reflected away from the substrate base to which the diode is attached because Led junction does not emit that much light. Due to this, the brightest light will be emitted at the top of the Led. [Image source]
Working Principle:
As we have mentioned above, a Light emitting diode is a PN junction. Hence its working principle is based on the same. Learn in detail, below.How LED Bulb Works
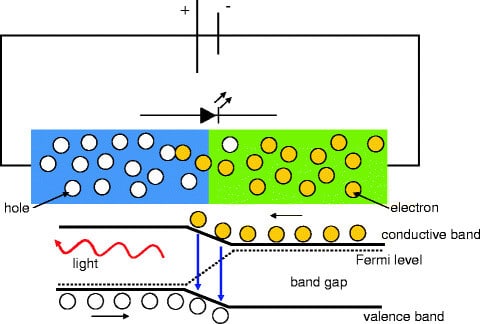
A Light emitting diode bulb consists of two semiconducting material i.e. p-type material and n-type material. A p-n junction is formed, by connecting these two types of materials.When the p-n junction is forward biased, the majority carriers; either electrons or holes; start moving across the junction.
As shown in the figure above, electrons start moving from n-region and holes start moving from p-region. When they moved from their regions they start to recombine across the depletion region. Free electrons will remain in the conduction band of energy level while holes remain in the valence band of energy level.
The Energy level of the electrons is high than holes because electrons are more mobile than holes i.e. current conduction due to electrons are more. During the recombination of electrons and holes, some portion of energy must be dissipated or emitted in the form of heat and light.
The phenomenon into which light emits from the semiconductor under the influence of the electric field is known as electroluminescence.
Always remember that the majority of light is produced from the junction nearer to the p-type region. So diode is designed in such a way that this area is kept close to the surface of the device to ensure that the minimum amount of light is absorbed.
The electrons dissipate energy in different forms depending on the nature of the diode used. Like for silicon and germanium diodes, it dissipates energy in the form of heat while for gallium phosphide (GaP) and gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) semiconductors, it dissipates energy by emitting photons. For the emission of different colors, different semiconductors are used. For example; phosphorus is used for a red light, gallium phosphide for the green light and aluminum indium gallium phosphide for yellow and orange light.Led Types:
Nowadays LEDs are the most used component in the electronics industry. It is available in a variety of sizes and shapes. There are different types of led lights available in the market as per the user requirement. Mainly Light Emitting Diodes are distinguished on the basis of the electrical property and the material used for their construction. Let’s have more insight below:- Depending on electrical properties:
- AC Driven: Without any need of DC converter these LEDs can operate on AC power. Seoul semiconductor released a high voltage LED namely Acrich MJT, capable of driving from AC power with a simple controlling circuit. An example of this type of Led is HP-LED has an efficacy of 40 lm/W.
- Miniature: Small size Light Emitting Diodes are mostly used these days because of its performance speed and good efficiency. For optical communications, efficient lightning, nano-lasers researchers have invented a thinnest Led made up of 2D flexible material which is 10 to 20 times thinner than 3D LEDs. Three main properties of miniature single die Led’s are low current typically rated for 2 mA, the ultra-high output of 20mA at apx 2V, 4V, or 5Vetc.
- High power: These type of Light Emitting Diodes can be driven at currents from hundreds of mA to more than an ampere. For heat dissipation, high power led must be mounted on a heat sink because if the heat from Hp-Led is not removed, it may cause damage to the device. It can be easily set in an array to form a powerful Led lamp.
- Depending on the material:
-
- Zinc selenide (ZnSe).
- Gallium Nitride( GaN)
- Gallium Phosphide (GaP)
- Silicon Carbide( SiC)
- Gallium Arsenide (Ga As)
- Gallium Arsenide Phosphide (Ga AsP)
Light Emitting Diodes Bulbs:
A LED bulb is a lighting device which uses Light emitting diodes to produce light when an electric current passes through it. These bulbs can work for 50000 hours if run within the specified temperature range. For replacement of 60W incandescent, these bulbs use 8-11 watts of power. The two main kinds of bulbs are: (a) Incandescent Bulb: It is a source of electric light into which filament connected is heated by passing an electric current. The filament used is made up of tungsten (a piece of metal) which got heated and glow the light when an electric current flows through it. As the metal glows, it gives out a bright white light. (b) Fluorescent bulb: These bulbs are the energy-saving bulbs known as the compact fluorescent light bulb. Inside it, a small amount of mercury is present which got vapourises when the electric current passes through it. As the gas is heated, particles bounce off a phosphorus coating that is applied to the internal section of the bulb which produces light.Advantages of LED lights:
Light emitting diodes have a variety of advantages over other light sources. Its advantages are:- Easily controlled and programmed.
- Large Life span.
- High efficiency.
- Low radiated heat.
- High levels of brightness and intensity.
- High reliability.
- No UV rays
- Low voltage and current requirements.
- Less wiring required.
- Low maintenance cost.
- Instant lightning.


Thank you so much for your kind information.
I need a article on white LED
Hi Sultana,
Glad you asked us. and Sorry for late reply. What exactly you need to know about White LED? Asking it so that we can cover it up in our article.
sir i have a question that
how to improve the lifetime of industrial using leds with low cost .
increasing the temperature is one of the main reason for less lifetime
please give any idea
Hi Sasidhar,
M happy you asked but the question is unclear. You want to improve lifetime of what thing?
THE INFORMATION ABOUT THE LIGHTS IS VERY WELL. I HAVE A QUESTION FOR YOU.
IF WE GIVE 5V , 2 mA SUPPLY FOR 4V RATED LED BULB THEN WHAT HAPPEND. PLEASE TELL ME.
Hi Mahaboob Basha,
Thanks for your question. Well if we pass 5V, 2mA current through 4v rated led bulb, then it will glow only when we connect a current limiting resistance in series. 2mA current is very low for any LED depending upon the colour of the led bulb, like the red led bulb requires minimum 5mA current & white led bulb requires 20mA.
Feel free to ask any question relating to electronics. Really appreciate your interest.
I loved it!
Thanks. Keep visiting for more information. 🙂